Nasa discovers 'super-Earth' exoplanet in habitable zone 137 light years away
According to Nasa, exoplanet was discovered by Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, launched in 2018
February 06, 2024
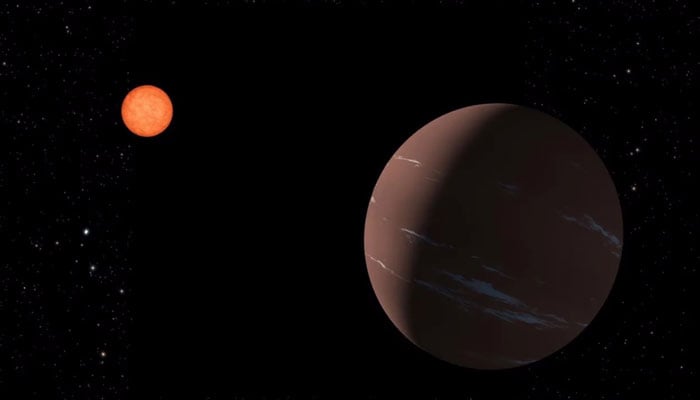
A "super-Earth" exoplanet, TOI-715 b, was discovered 137 light-years away from Earth, prompting further exploration into its life-sustaining conditions, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (Nasa) announced.
Nasa confirmed that scientists found the planet — about one and a half times as wide as Earth — orbits within a conservative "habitable zone" around its parent star.
The space agency defines a habitable zone as the distance from a star that allows liquid water to form on a planet's surface.
Astronomers noted that other factors are also necessary for a suitable atmosphere, though the planet’s placement in the zone puts it in a "prime position" from its parent star, The Hill reported.
The parent star of the planet is a red dwarf with a tighter orbit, allowing it to "crowd closer" and have a year of 19 Earth days, making it easier to detect and more frequently observed, according to the agency.
According to Nasa, the planet was discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), launched in 2018.
TESS has discovered a series of other habitable zone exoplanets that can be more closely observed by Nasa’s James Webb Space Telescope.
A second planet, the size of Earth, may also be part of the newfound system, and it may be located just inside the conservative habitable zone.
Nasa said that if this is verified, it will be the smallest planet in the habitable zone that TESS has found yet.











