Smog-choked Lahore leads global pollution rankings with dangerous air quality
Lahore’s AQI surges past 1,000, tops real-time list of world’s most polluted cities
November 02, 2024
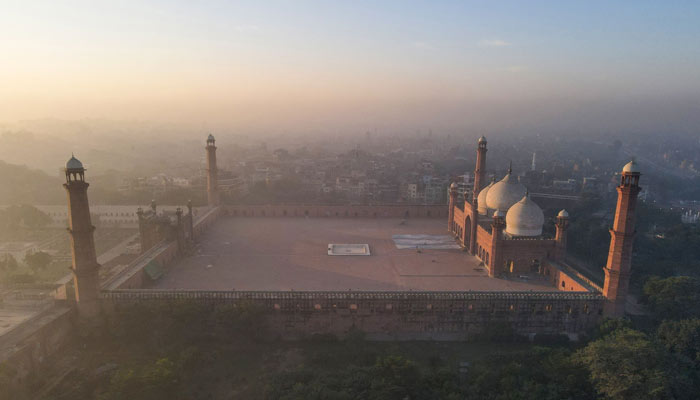

- Pollution-led smog in city causes serious problems for residents.
- Seasonal crop burn-off by farmers on suburbs adds to toxic air.
- Delhi's air quality improves day after topping global pollution charts.
Punjab’s capital Lahore choked on toxic smog, ranking first on the list of most polluted cities in the world once again on Saturday as the air quality continues to deteriorate in the megapolis.
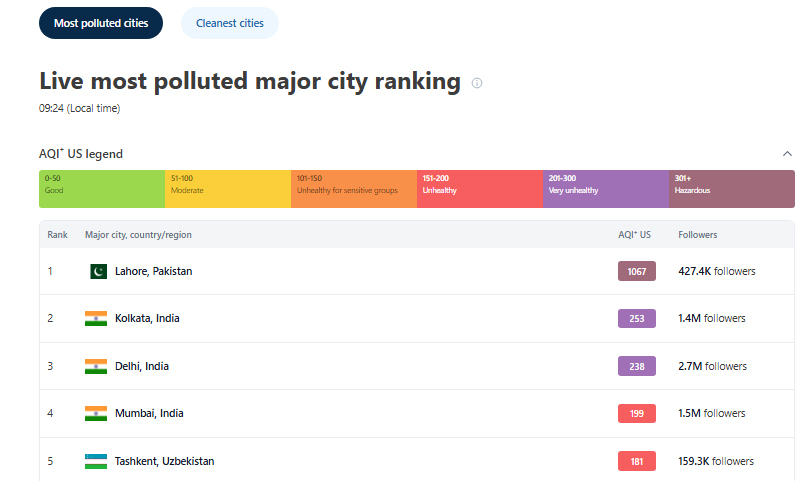
The air quality index (AQI) in Lahore surged to 1,067 around 9:30am on a real-time global pollution chart by Swiss air quality watchdog, despite the provincial government's desperate attempts to fight off smog.
Terming it “record high”, Jahangir Anwar, a senior environmental protection official in Lahore, said: "We have never reached a level of 1,000."
"The air quality index will remain high for the next three to four days," he added.
The city battles smog— a mix of fog and pollutants caused by low-grade diesel fumes — each year in winter. Seasonal crop burn-off by farmers on the outskirts of Lahore also contributes to toxic air, which according to the World Health Organisation (WHO), can cause strokes, heart disease, lung cancer besides respiratory diseases.
Earlier this week, the provincial environmental protection agency announced new restrictions in four "hot spots" in the city.
Tuk-tuks equipped with polluting two-stroke engines have been banned while government offices and private companies will have half their staff work from home from Monday.
Construction work has been halted and street and food vendors, who often cook over open fires, ordered to close by 8 pm.
Meanwhile, visibility was reduced to zero in the megapolis following the rise in smog levels.
However, the AQI improved to 702 by 10:30am, and later to 283 but Lahore retained its position on the top.
Weather experts predicted that the intensity of smog will persist during the next 48 hours. They said the smoke-laden air from the Indian capital New Delhi had contributed to increase in smog levels.
Pollution-led smog in the city is causing serious problems for residents, especially those who work outdoors. Citizens toiling in polluted air have reported breathing difficulties, coughing and burning eyes, affecting both their health and productivity.
"It's been tough to breathe and I've fallen sick two times this month. We can't go out without masks and we can't work effectively either," Lahore resident Mohammad Saad, 30, told Geo.tv.
Keeping in view the situation, Punjab has imposed a "Green Lockdown" in the most polluted zones of Lahore to combat rising smog levels.
The restrictions imposed in the areas identified as air pollution hotspots, included a complete ban on construction activities, entrance of "Qingqi motorcycle-rickshaws", operation of commercial generators, open food cooking points and food outlets using charcoal, coal or wood without installation of proper emission control system.
The government also introduced mandatory mask-wearing and restricted outdoor activities, including school assemblies and playtime to keep the citizens safe from severe smog.
However, the measures appear ineffective in mitigating the impact of smog as its continues to rise across Punjab, causing a sharp deterioration in air quality.
The central and southern regions of the province were also engulfed in harmful smog. Thickening smog in Multan and surrounding areas is creating further difficulties for residents.
Pollution in excess of levels deemed safe by the WHO shortens the life expectancy of Lahore residents by an average of 7.5 years, according to the University of Chicago's Energy Policy Institute.
Children are particularly vulnerable because they have less developed lungs and breathe more rapidly, taking in more air relative to their size than adults.
According to UNICEF, nearly 600 million children in South Asia are exposed to high levels of air pollution.
Neighbouring India, where the capital city New Delhi also reels under intensifying smog has called for collaboration and regional cooperation in South Asia to tackle the deteriorating air pollution dilemma after Punjab Chief Minister Maryam Nawaz floated the idea of engaging in diplomatic efforts with India.
Delhi ranked first on the most polluted cities' list on Friday, after revellers defying a ban on firecrackers to celebrate Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights, helped drive air quality to hazardous levels.
Today, the air quality in the Indian capital marked improvement as the city ranked third on the pollution charts with an AQI of 238, as per IQ Air. Eastern city Kolkata had the second worst air quality in the world this morning.
Additional input from AFP.











